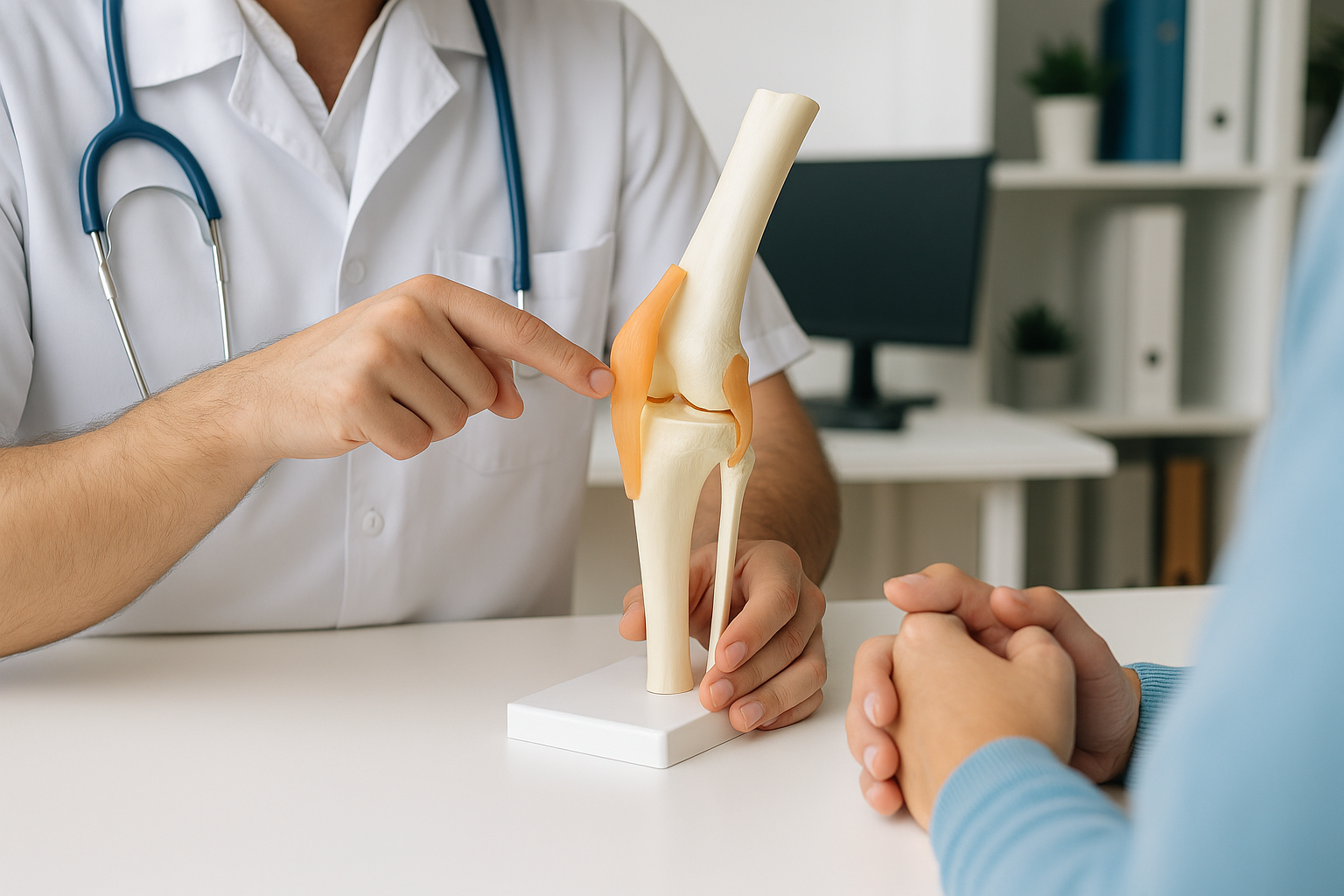
Orthopedics
- WHAT IS ORTHOPEDICS AND WHICH CONDITIONS DOES IT TREAT?
- HOW ARE JOINT DISEASES AND OSTEOARTHRITIS TREATED?
- HOW ARE FRACTURES AND TRAUMATIC INJURIES MANAGED SURGICALLY?
- WHAT ARE THE TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR SPINE AND DISC PROBLEMS?
- HOW ARE SPORTS INJURIES DIAGNOSED AND TREATED?
- WHAT IS JOINT REPLACEMENT SURGERY AND WHEN IS IT NECESSARY?
- HOW ARE SHOULDER, ARM, AND TENDON INJURIES TREATED?
- WHAT IS THE RECOVERY PROCESS AFTER ORTHOPEDIC SURGERY?
Orthopedics is a medical specialty dedicated to diagnosing, treating, and preventing disorders of the musculoskeletal system, which includes bones, joints, muscles, ligaments, tendons, nerves, and the spine. These structures work together to support movement, stability, posture, and overall physical function. Problems in any part of this system can lead to pain, stiffness, deformity, loss of strength, or significant limitations in daily life.
Orthopedic conditions may arise from various causes, including aging, accidents, sports injuries, congenital abnormalities, overuse, infections, or degenerative diseases such as osteoarthritis. The field covers a broad range of problems, from joint pain and inflammation to fractures, spinal disorders, soft tissue injuries, and complex deformities.
Diagnosis begins with a detailed physical examination supported by advanced imaging methods such as X-rays, MRI, CT scans, ultrasound, and laboratory evaluations when necessary. A precise diagnosis ensures that treatment can be tailored to the patient’s condition and lifestyle.
Treatment options range from conservative approaches—such as medication, rest, bracing, and physical therapy—to minimally invasive procedures and advanced surgical interventions. These surgeries may involve repairing damaged tissues, stabilizing fractures, correcting deformities, or replacing worn-out joints with prosthetic implants.
The primary goal of orthopedic care is to restore mobility, relieve pain, improve joint and muscle function, and help patients return to their daily activities safely and with better quality of life. At OFM Hospital, our orthopedic team combines modern technology with evidence-based medical practice to deliver comprehensive and personalized care to every patient.
Joint diseases, particularly osteoarthritis, are among the most common causes of chronic pain and mobility limitations in adults. Osteoarthritis occurs when the protective cartilage covering the ends of bones gradually wears down, leading to stiffness, swelling, grinding sensations, and reduced range of motion. Although it typically affects weight-bearing joints such as the knees and hips, it can also involve the shoulders, hands, spine, and ankles.
Diagnosis begins with a comprehensive clinical examination, including assessment of joint movement, stability, and pain patterns. Imaging techniques such as X-ray, MRI, or ultrasound help determine the severity of cartilage loss, presence of bone spurs, and overall joint condition. These findings allow orthopedic specialists to tailor treatment to the patient’s specific needs.
Early-stage osteoarthritis is typically managed with non-surgical treatments, which may include pain-relieving and anti-inflammatory medications, joint-supporting supplements, physiotherapy, muscle-strengthening exercises, and weight management strategies. Lifestyle adjustments—such as low-impact activities, proper footwear, and reducing joint load—play a key role in slowing disease progression.
For patients requiring additional support, injection therapies can provide significant relief. Options include corticosteroid injections to control inflammation, hyaluronic acid injections to improve lubrication, and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) or regenerative treatments to promote tissue healing in selected cases.
When conservative treatments are no longer effective and joint damage becomes severe, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgical options vary from minimally invasive procedures such as arthroscopy—used to clean the joint, remove loose fragments, or repair damaged tissues—to more advanced reconstructive surgeries. In advanced osteoarthritis, joint replacement (arthroplasty) may be recommended, especially for the knee, hip, or shoulder. This procedure replaces the worn-out joint surfaces with durable prosthetic components, restoring smooth movement and reducing pain dramatically.
With appropriate treatment and follow-up, most patients experience a significant improvement in mobility, joint comfort, and quality of life. At OFM Hospital, we offer a full range of orthopedic treatment options designed to meet each patient’s functional goals and lifestyle needs.
Fractures and traumatic injuries are among the most urgent conditions treated in orthopedics. They occur as a result of accidents, falls, sports injuries, or high-impact trauma, and can affect any bone in the body. The severity of a fracture depends on factors such as bone displacement, fragmentation, involvement of the joint surface, and the condition of surrounding tissues like muscles, nerves, and blood vessels.
The treatment process begins with a detailed clinical evaluation and advanced imaging—typically X-ray or CT scans—to determine the exact location and pattern of the fracture. Once the diagnosis is clear, the orthopedic surgeon decides whether the injury can be managed non-surgically or requires surgical intervention. Stable fractures may be treated with casting, splinting, or bracing, but unstable, displaced, or joint-involving fractures often need surgery to restore normal alignment and prevent long-term functional problems.
Surgical treatment varies depending on the type of fracture. Open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) is one of the most commonly used methods, involving precise repositioning of the broken bone and fixation with plates, screws, or rods. For long bone fractures such as the femur or tibia, intramedullary nailing provides strong stabilization and allows earlier mobilization. In cases where bones cannot be adequately stabilized internally, external fixation may be used to secure the fracture with a frame outside the body. Complex joint fractures—including those of the ankle, wrist, shoulder, and elbow—often require meticulous reconstruction to restore joint surfaces and prevent post-traumatic arthritis.
Soft tissue injuries associated with fractures—such as torn ligaments, tendon damage, or nerve involvement—are evaluated carefully and repaired when necessary to ensure full functional recovery. Minimally invasive techniques are preferred whenever possible to reduce surgical trauma, minimize infection risk, and promote faster healing.
Rehabilitation plays a crucial role after fracture surgery. Early physiotherapy helps maintain joint flexibility, strengthen muscles, and prevent stiffness. Weight-bearing guidelines depend on the type of fracture and the fixation method used. Follow-up imaging is performed regularly to monitor bone healing and ensure the fixation remains stable. With proper care, most patients achieve excellent long-term outcomes and return to their daily activities without limitations.
At OFM Hospital, our trauma and orthopedic team provides comprehensive fracture management using modern surgical techniques, advanced implants, and personalized rehabilitation plans to ensure safe and successful recovery.
Spine and disc disorders are among the most common causes of chronic pain, mobility limitations, and neurological symptoms in adults. These conditions can affect the cervical (neck), thoracic (mid-back), or lumbar (lower back) regions and often arise from aging, degenerative changes, trauma, poor posture, herniated discs, or narrowing of the spinal canal. When left untreated, spine problems can lead not only to persistent pain but also to numbness, weakness, or coordination difficulties due to nerve compression.
Diagnosis begins with a thorough physical examination, neurological assessment, and advanced imaging such as MRI, CT scans, and X-rays. These tests help identify disc herniation, spinal stenosis, nerve root compression, vertebral instability, or degenerative disc disease. A clear diagnosis allows the orthopedic team to design an individualized treatment plan.
Most patients benefit from non-surgical treatments initially. These may include anti-inflammatory medications, muscle relaxants, physiotherapy, core-strengthening exercises, posture correction, and structured rehabilitation programs. For patients experiencing severe nerve-related pain, epidural steroid injections, facet joint injections, and nerve root blocks can provide significant relief. These minimally invasive procedures help control inflammation and reduce pressure on irritated nerves.
When conservative treatments fail or when significant neurological deficits appear—such as muscle weakness, loss of sensation, or bladder/bowel dysfunction—surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgical options depend on the underlying condition.
-
Microdiscectomy is commonly performed for herniated discs and involves removing the portion of the disc pressing on the nerve.
-
Laminectomy or laminotomy may be used for spinal stenosis to relieve pressure on the spinal canal.
-
Spinal fusion surgery is considered when instability or severe degeneration is present, helping to stabilize vertebrae and reduce mechanical pain.
-
In carefully selected cases, artificial disc replacement can restore mobility while removing the damaged disc.
Modern spine surgery at OFM Hospital focuses on minimally invasive techniques whenever possible. These approaches reduce tissue damage, shorten hospital stays, and promote faster recovery. After surgery, rehabilitation is essential to restore flexibility, strengthen supporting muscles, and prevent recurrence.
Long-term spine health requires lifestyle adjustments, including maintaining good posture, avoiding heavy lifting, managing body weight, and staying physically active. Regular medical follow-up ensures that nerve healing, spinal alignment, and overall function progress as expected.
With precise diagnosis, advanced surgical techniques, and personalized rehabilitation, most patients experience significant improvements in pain, mobility, and overall quality of life.
Sports injuries occur when muscles, ligaments, tendons, joints, or bones are subjected to sudden impact, excessive strain, or repetitive overuse. These injuries can affect professional athletes, active individuals, or even beginners starting a new activity. Common conditions include ligament tears, meniscus injuries, muscle strains, tendonitis, shoulder instability, ankle sprains, stress fractures, and cartilage damage. Without proper diagnosis and treatment, these problems can lead to chronic pain, reduced performance, and long-term functional limitations.
Evaluation begins with a detailed history of how the injury occurred, followed by physical examination focusing on swelling, range of motion, joint stability, and strength. Advanced imaging tools—such as MRI, ultrasound, and X-rays—play a key role in identifying soft tissue tears, cartilage damage, or bone involvement. Accurate assessment allows orthopedic specialists to design a treatment plan tailored to the athlete’s level of activity and goals.
Most sports injuries are managed initially with non-surgical treatments, including rest, ice, compression, elevation (RICE), anti-inflammatory medications, and targeted physiotherapy. Rehabilitation programs are essential for restoring flexibility, muscle balance, coordination, and proper biomechanics. Strengthening exercises and neuromuscular training help prevent re-injury and support safe return to sports.
For injuries that involve significant structural damage—such as complete ACL tears, severe meniscus injuries, or shoulder dislocations—surgical intervention may be required to restore joint stability and athletic function. Modern arthroscopic techniques allow surgeons to repair or reconstruct damaged tissues through small incisions, resulting in less pain, faster healing, and quicker return to physical activity. Procedures such as ACL reconstruction, meniscus repair, labrum repair, and cartilage microfracture are commonly performed using minimally invasive methods.
Recovery after sports-related surgery involves a structured rehabilitation program supervised by physiotherapists. Rehabilitation phases typically include controlled mobility, progressive strengthening, balance exercises, gait training, and sport-specific drills. The goal is to help the patient safely regain full strength, flexibility, and performance capacity.
At OFM Hospital, our orthopedics and sports medicine team provides comprehensive care for athletes of all levels. Using advanced diagnostics, minimally invasive surgical techniques, and personalized rehabilitation strategies, we help patients return to their sport stronger, safer, and with reduced risk of future injuries.
Joint replacement surgery, also known as arthroplasty, is a highly effective procedure designed to relieve severe joint pain, restore mobility, and improve overall quality of life when the natural joint can no longer function properly. It is most commonly performed on weight-bearing joints such as the hip, knee, and shoulder, but may also be recommended for elbows or ankles in select cases. The operation involves removing the damaged or worn-out joint surfaces and replacing them with durable artificial components made of metal, ceramic, or high-grade polyethylene.
The most frequent reason for joint replacement is advanced osteoarthritis, where cartilage has deteriorated to the point that bones rub directly against each other. This leads to persistent pain, stiffness, swelling, and significant movement limitations. Other causes include rheumatoid arthritis, avascular necrosis, post-traumatic joint degeneration, congenital deformities, or long-term structural damage following previous injuries.
Before deciding on surgery, orthopedic specialists perform a comprehensive assessment that includes physical examination, detailed imaging studies (X-ray, MRI, or CT scans), gait analysis, and evaluation of daily functional needs. Patients are typically advised to consider joint replacement when conservative treatments—such as medications, physiotherapy, injection therapies, bracing, or lifestyle modifications—no longer provide meaningful relief.
Modern joint replacement surgery is performed using advanced techniques that prioritize precision, minimal tissue damage, and long-lasting results. In many cases, minimally invasive approaches are used to reduce recovery time and postoperative discomfort. Prosthetic implants are engineered to mimic natural joint movement, offering excellent durability and smooth motion.
The postoperative period involves controlled mobilization, pain management, and a structured physiotherapy program. Early rehabilitation focuses on improving joint range of motion, building muscle strength, and restoring functional mobility. Most patients begin walking within a day of surgery, depending on the joint replaced and the surgical technique used. Over the following weeks, progressive therapy helps patients regain independence and resume daily activities safely.
When performed at the right time and by an experienced team, joint replacement surgery provides dramatic improvements in pain relief, stability, and overall physical performance. At OFM Hospital, our orthopedic surgeons use high-quality prosthetic materials, advanced surgical navigation systems, and personalized rehabilitation plans to ensure optimal long-term outcomes.
Shoulder, arm, and tendon injuries are common problems that affect people of all ages, often leading to pain, weakness, and limitations in daily activities. These injuries may result from sudden trauma, repetitive motion, overuse, sports activities, or age-related degeneration. The shoulder, in particular, is one of the most mobile joints in the body—making it both highly functional and vulnerable to instability and soft tissue injuries.
The most frequently encountered conditions include rotator cuff tears, shoulder impingement, biceps tendon injuries, frozen shoulder, calcific tendonitis, elbow ligament injuries, and tendon strains in the arm or forearm. Patients may experience pain during lifting or overhead movements, reduced range of motion, clicking sensations, or difficulty performing simple tasks such as reaching behind the back.
Diagnosis of these injuries involves a detailed physical examination to assess strength, stability, and joint mobility, followed by imaging such as ultrasound or MRI to evaluate soft tissue damage. These tests help determine whether the injury can heal conservatively or requires surgical intervention.
Many tendon and shoulder problems can be treated with non-surgical methods, especially in early stages. These include rest, activity modification, anti-inflammatory medications, ice therapy, physiotherapy, stretching exercises, strengthening programs, and posture correction. Injection therapies—such as corticosteroids or PRP (platelet-rich plasma)—may also help reduce inflammation and support tissue healing.
When tears are significant, symptoms persist despite conservative care, or the joint becomes unstable, surgical treatment may be necessary. Modern orthopedic techniques often use arthroscopy, a minimally invasive method that allows surgeons to repair ligaments, reattach tendons, remove inflamed tissue, or smooth bone surfaces through tiny incisions. Rotator cuff repair, labrum repair, biceps tendon stabilization, and elbow tendon reconstruction are common arthroscopic procedures.
After surgery, rehabilitation plays a crucial role in restoring normal function. Early stages focus on gentle mobility and pain control, followed by progressive strengthening and stability exercises. Full recovery varies depending on the type of injury and repair, but most patients regain excellent shoulder and arm function with a structured therapy program.
At OFM Hospital, our orthopedic specialists provide comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment plans for all types of shoulder, arm, and tendon injuries—helping patients return safely to their daily activities, work routines, and sports.
Recovery after orthopedic surgery is a structured process designed to restore mobility, reduce pain, and help patients safely return to their daily activities. The exact timeline varies depending on the type of procedure—such as fracture fixation, tendon repair, spine surgery, or joint replacement—but all orthopedic surgeries follow fundamental healing principles supported by modern rehabilitation techniques.
The postoperative period typically begins in the recovery room, where vital signs, limb circulation, and pain levels are closely monitored. In many cases, patients begin gentle movement or breathing exercises shortly after surgery to prevent complications such as stiffness, blood clots, or lung congestion. Pain management is carefully planned using medications, ice therapy, and sometimes nerve blocks to ensure comfort and support early mobility.
Once the patient stabilizes, a personalized rehabilitation program is initiated. Physiotherapy is a cornerstone of the recovery process. Early-stage therapy focuses on controlled joint mobility, maintaining flexibility, and preventing muscle loss. As healing progresses, rehabilitation shifts toward strengthening exercises, balance training, gait correction, and functional tasks tailored to the patient’s lifestyle and activity goals.
Assistive devices—such as walkers, crutches, slings, or braces—may be needed temporarily to protect the surgical area and ensure safe movement. The orthopedic team provides detailed instructions on weight-bearing limitations, wound care, medication schedules, and daily activity modifications.
Follow-up appointments are essential for tracking the healing process. X-rays, ultrasound, or physical assessments help ensure bones are uniting correctly, tendons are healing, implants remain stable, and there are no signs of infection or complications. These visits also allow the medical team to adjust the rehabilitation plan and address patient concerns promptly.
Lifestyle adjustments play a key role in long-term recovery. Adequate nutrition, hydration, smoking cessation, posture correction, and gradual return to physical activity help optimize healing and protect the repaired structures. For joint surgeries or complex repairs, patients may enroll in longer rehabilitation programs to restore full strength and function.
With proper postoperative care, adherence to rehabilitation, and regular medical follow-up, most patients experience significant improvements in mobility, stability, and overall quality of life. At OFM Hospital, we prioritize safe recovery through evidence-based surgical techniques, advanced rehabilitation protocols, and personalized patient support.
Specialist Dr. Şakir Özdemir
Specialist Dr. Şakir Özdemir
Trakya University Faculty of Medicine
Istanbul Vakıf Gureba Training and Research Hospital – Psychiatry Specialist
Private OFM Hospital, Antalya
Department: Psychiatry
Education: Trakya University Faculty of Medicine
E-mail: sakir.ozdemir@ofmantalya.com
Languages: English
-
2008–2010: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy – Prof. Dr. Mehmet Zihni Sungur
-
2008–2010: Psychodynamic-Oriented Psychotherapy – Prof. Dr. Doğan Şahin
-
2008–2010: Sexual Dysfunction Therapy, CETAD Modules 1-2-3, Supervision (8 weeks)
-
2017: Alcohol and Substance Addiction Training – Republic of Turkey, Ministry of Health
-
Depression
-
Panic Disorders
-
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorders (OCD)
-
Personality Disorders
-
Social Phobia (Social Anxiety Disorder)
-
Sexual Function Disorders
-
Mood Disorders
-
Schizophrenia
-
Turkish Medical Association
-
Turkish Psychiatric Association