General Surgery
Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is the most common and leading cause of cancer-related deaths among women worldwide.
Globally, the number of newly diagnosed patients exceeds 2 million.
It accounts for more than 20% of all female cancers and 15% of cancer-related deaths among women.
According to current data, it is estimated that one out of every eight women will develop breast cancer during her lifetime.
Risk Factors for Breast Cancer
-
Advanced age (>50 years)
-
Early menarche (<12 years)
-
Late menopause (>55 years)
-
Never having given birth
-
Not having breastfed
-
Giving birth at an advanced age (>35 years)
-
Childhood radiotherapy applied to the thoracic region
-
Long-term postmenopausal hormone replacement therapy
-
Long-term use of oral contraceptives
-
Chronic alcohol consumption
-
Previous biopsy results showing pre-cancerous cells
Among genetic risk factors, the most common are BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutations.
These genes are involved in DNA repair, and their mutation predisposes individuals to breast and ovarian cancers.
Diagnosis and Screening
The most effective imaging methods for breast cancer screening and diagnosis are mammography and breast ultrasonography.
Additionally, breast MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) may be used, but it should not be the first choice.
MRI should only be used when mammography and ultrasonography are inconclusive.
It is useful in investigating occult breast tumors, dense tissue, multifocality, multicentricity, and in follow-up after breast-conserving surgery to differentiate scar from recurrence.
MRI is also used to evaluate the response to chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
Biopsy Methods
Four techniques are used to perform a biopsy from a defined breast lesion:
-
Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy (FNAB)
-
Core Needle Biopsy (CNB)
-
Vacuum-Assisted Biopsy (VAB)
-
Open Surgical Biopsy
Patients diagnosed with breast cancer should be clinically staged before starting treatment.
The TNM system is used to determine tumor size (T), nodal status (N), and metastasis (M).
This system helps define prognosis and treatment decisions.
Clinical Staging
Clinical staging requires:
-
Medical history (anamnesis)
-
Physical examination
-
Radiological and laboratory investigations
Systemic spread should be evaluated with PET-CT, thorax/abdominal CT, bone scintigraphy, and brain MRI.
Before surgery, histopathological diagnosis, neoadjuvant chemotherapy, and Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy (SLNB) indications should be carefully reviewed.
Surgical Approach
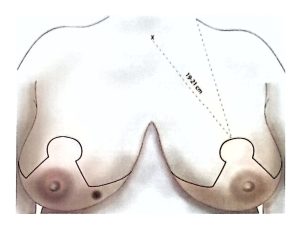
In patients considered suitable for Breast-Conserving Surgery (BCS), breast MRI can be used to evaluate dense tissue and multifocality.
Since synchronous tumors can occur in the opposite breast, both sides must be carefully examined.
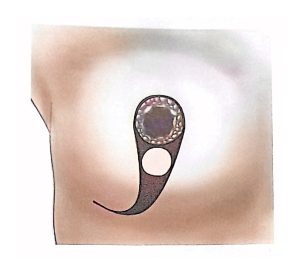
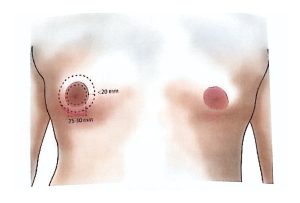
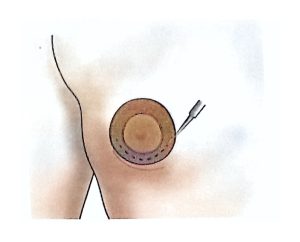
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy (SLNB) is performed during surgery in patients without clinically evident axillary lymph node metastasis.
Sentinel nodes (the first lymph nodes draining the tumor area) are identified and removed for pathological examination.
If no metastasis is detected, axillary dissection can be avoided, reducing morbidity.
Treatment Approaches
Comparative studies show that survival rates are equal between simple mastectomy, breast-conserving surgery, and modified radical mastectomy.
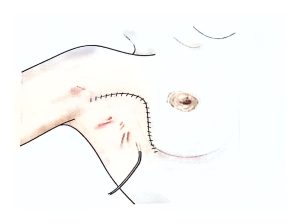
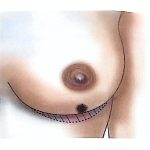
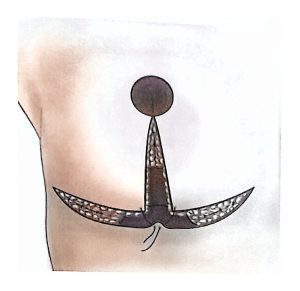
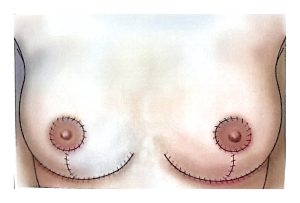
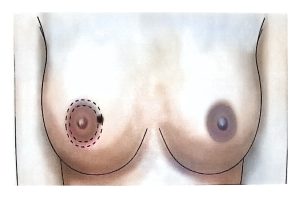
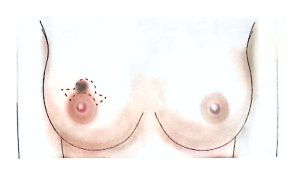
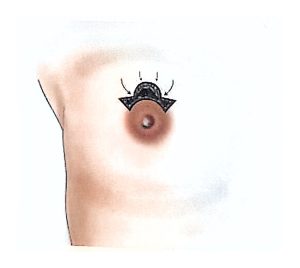
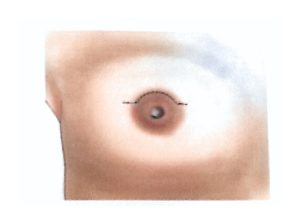
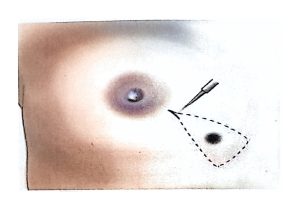
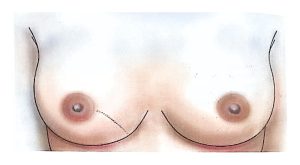
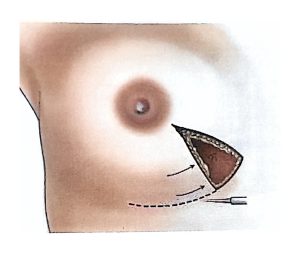
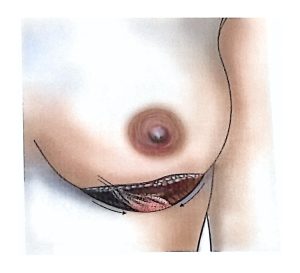
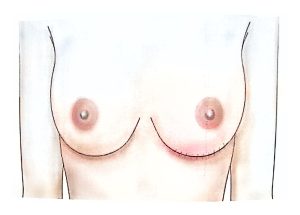
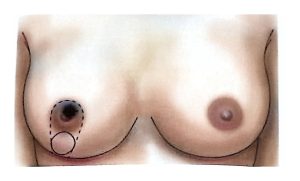
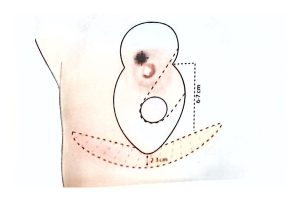
Therefore, modern surgical treatment emphasizes Breast-Conserving Surgery (BCS) and Oncoplastic Breast Surgery (OPS), which combine oncologic safety with aesthetic reconstruction.
OPS provides better cosmetic results and has a positive psychological impact on patients.
With advances in surgical techniques, OPS has become a safe and effective procedure in experienced hands.
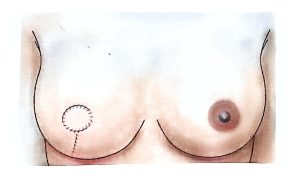
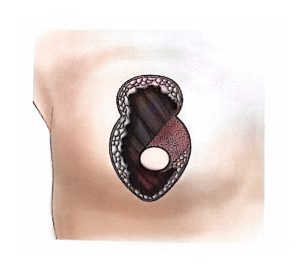
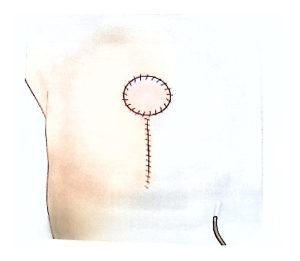
BCS may also be called segmentectomy, lumpectomy, partial mastectomy, or wide local excision.
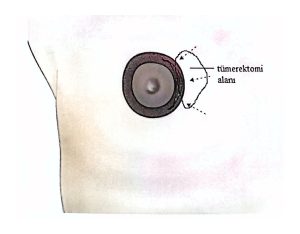
It involves removing the tumor along with a rim of healthy tissue to ensure clear margins.
OPS combines oncologic and plastic surgery techniques to achieve both definitive and aesthetic results in a single operation, reducing post-mastectomy stress and improving recovery.
Postoperative Outcome
With the integration of oncoplastic reconstruction, breast cancer surgery now ensures both oncologic safety and aesthetic satisfaction.
These methods not only improve cosmetic results but also enhance the patient’s psychological recovery process and quality of life.


Breast Cancer Statistics and Risk Factors
Important information about breast cancer has been shared. When breast cancer is examined historically, it is seen that this disease appears even in the earliest surgical documents dating back to 3000–2500 BC. Interestingly, the patient mentioned in these documents was a man, and the phrase “there is no cure” was used. Perceptions related to this disease changed over time, as the tumor resembled a spider web or strands of yarn, and surgical removal of the breast tissue and axillary lymph nodes was risky until the early 1800s.
Breast cancer is the most common type of cancer in women both worldwide and in our country. About one-third of all cancers seen in women originate from breast cancer. According to current data, one out of every eight women faces a breast cancer diagnosis at some point in her life. The incidence of breast cancer in women is about 100 times higher than in men. In recent years, there has also been an increase in the frequency of breast cancer in men, which is related to tumor type and delays in diagnosis.
When risk factors are examined, it is seen that in addition to genetic factors (such as BRCA1-2, p53 gene mutations), environmental factors are also important. Having a family history of breast cancer or first-degree relatives with a history of breast cancer are among the factors that increase the risk. Early menstruation, late menopause, a history of radiotherapy to the breast area, obesity, irregular nutrition, and lack of physical activity are also factors that increase the risk of breast cancer.
Symptoms and Early Diagnosis
Symptoms of breast cancer include swelling, retraction, or dimpling of the breast skin, non-healing wounds or redness, peeling or crusting of the nipple skin, nipple discharge, nipple deformity, and a palpable lump in the breast or armpit. These symptoms, which usually occur without pain, may prevent many women from considering consulting a General Surgery Specialist. However, it is important to note that there is no definite relationship between pain and breast cancer, as pain is more often a symptom of benign tumors.
Early Diagnosis and Treatment Approaches
Early diagnosis plays a critical role in the treatment of diseases such as breast cancer. For this reason, monthly self-breast examination, regular check-ups by a General Surgery Specialist, and screenings using imaging methods (Breast Ultrasound, Digital Mammography, Breast MRI) are recommended. In suspicious cases, biopsy methods are used for pathological examination, and the stage of the disease is determined. Treatment methods include surgical intervention, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and oncological treatments. Thanks to early diagnosis, breast cancer has become a disease that can be prevented and treated with modern medical methods.
Conclusion
Breast cancer is a disease that can be effectively controlled through early diagnosis and modern medical approaches. It is important for women to perform regular self-examinations, live a healthy life by considering risk factors, and protect their breast health through regular check-ups. It should not be forgotten that early diagnosis is one of the critical steps in the treatment process of this cancer.
Breast cancer is one of the most common types of cancer in women. Early diagnosis and effective treatment are important steps in the fight against cancer. However, we also do not ignore our patients’ need to return to their daily lives and feel better at the end of the treatment process.
Oncoplastic Surgery is an approach that focuses on preserving breast tissue as part of breast cancer treatment and performing aesthetic corrections after the fight against cancer.
Advantages of Oncoplastic Surgery:
🌺 Preservation of breast tissue and achievement of aesthetically pleasing results
🌺 Improvement of physical appearance after cancer treatment
🌺 Enhancement of our patients’ quality of life
We share this information with you to raise awareness about the importance of taking care of our health and early diagnosis. Remember, breast cancer can be treated with early detection!


